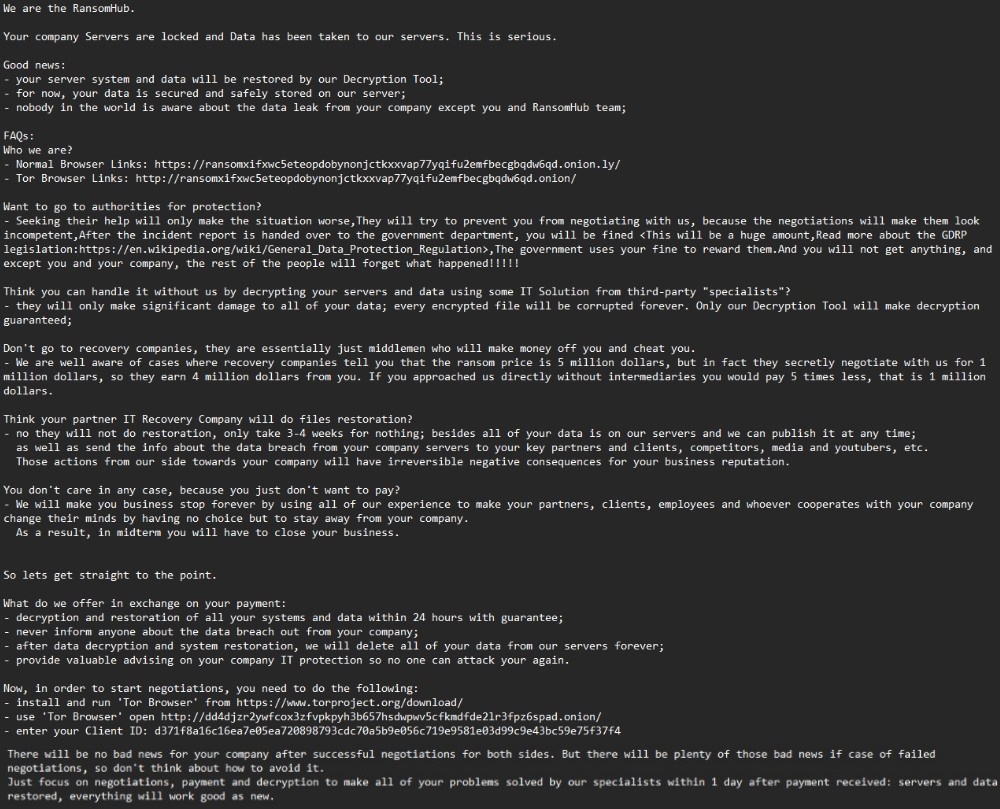
RansomHub emerges as a significant ransomware menace in 2024, focusing on 600 organizations after ALPHV and LockBit disruptions. Group-IB reveals its speedy rise in cybercrime.
Group-IB’s newest analysis, shared completely with Hackread.com, highlights the sudden rise of ransomware-as-a-service operations, with one group being very energetic on this area, recognized as RansomHub. Rising in early 2024, RansomHub rapidly established itself as a significant participant, capitalizing on the disruption of different distinguished teams like ALPHV and LockBit.
Group-IB’s investigation reveals that RansomHub strategically advertises its partnership program on underground boards just like the RAMP discussion board, actively recruiting associates from disbanded ransomware operations, which helps them quickly broaden their attain and impression.
Additional investigation means that RansomHub probably acquired its ransomware and internet software supply code from the Knight group (aka Cyclops), demonstrating the interconnected nature of the world of cybercrime. By leveraging current assets, RansomHub accelerated its growth and deployment, rapidly turning into a major menace. Their ransomware is designed for cross-platform compatibility, focusing on numerous working techniques and architectures, together with Home windows, ESXi, Linux, and FreeBSD. This versatility permits them to maximise their potential targets.
RansomHub’s operations replicate a excessive diploma of sophistication. They make the most of superior methods, reminiscent of exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities and using instruments like PCHunter to bypass endpoint safety options. Their adaptability is clear of their speedy weaponization of newly found vulnerabilities, usually outpacing defenders’ capacity to patch techniques. Additionally they reveal proficiency in conventional assault strategies, reminiscent of brute-force assaults towards VPN providers when vital.
Following preliminary reconnaissance and exploitation of vulnerabilities, they set up persistence throughout the compromised community and proceed with inner reconnaissance, figuring out and focusing on essential property like network-attached storage (NAS) and backup techniques. Knowledge exfiltration is a key goal, with instruments like Filezilla used to switch delicate info to exterior command and management servers.
The ultimate stage of a RansomHub assault usually includes knowledge encryption and extortion. They disable backup providers and deploy ransomware to render knowledge inaccessible, successfully crippling the sufferer group. The ransomware itself boasts superior options, together with the flexibility to terminate digital machines, delete shadow copies, and clear system occasion logs. This complete strategy goals to maximise the impression of the assault and enhance the probability of a ransom fee.
In response to Group-IB’s report, totally different variants of the ransomware are tailor-made for particular platforms, every with its personal set of command-line choices. The Home windows variant, specifically, affords intensive management over execution, together with secure mode execution and community spreading capabilities.
“RansomHub has focused over 600 organizations globally, spanning sectors reminiscent of healthcare, finance, authorities, and demanding infrastructure, firmly establishing it as essentially the most energetic ransomware group in 2024.”
Group-IB
A selected RansomHub assault, lasting underneath 14 hours, was investigated by Group-IB. The attackers initially exploited a vulnerability in a Palo Alto firewall (CVE-2024-3400) after which brute-forced VPN credentials to achieve entry. They then compromised the area controller utilizing vulnerabilities CVE-2021-42278 (sAMAccount Spoofing) and CVE-2020-1472 (ZeroLogon) to achieve management, moved laterally throughout the community accessing NAS servers and shared folders, and exfiltrated knowledge utilizing Filezilla.
The assault culminated in disabling backups, deploying ransomware, and finally encrypting essential knowledge. The attackers then left, forsaking traces of their exercise, which Group-IB’s DFIR crew investigated additional. This assault sequence, from preliminary compromise to remaining knowledge encryption, is visually represented on this picture by Group-IB.
This highlights the significance of patching recognized vulnerabilities, as emphasised by Martin Jartelius, CISO at Outpost24: “It’s troublesome to victim-blame with regards to zero-day exploits or provide chain breaches, however when a company is hit by a vulnerability that has been patched for over 4 years, it’s clear that somebody throughout the crew has knowingly taken on a major threat,” defined Martin.
“The kill chain doesn’t start with this exploit; it begins with preliminary entry. Organizations should concentrate on hardening their exterior assault floor and coaching employees to cut back the probability of breaches. Leaving techniques unpatched or deliberately susceptible is a severe safety misstep.”