Outpost24’s KrakenLabs reveals EncryptHub’s multi-stage malware marketing campaign, exposing their infrastructure and techniques by crucial OPSEC failures. Learn the way this rising cybercriminal group operates and the threats they pose.
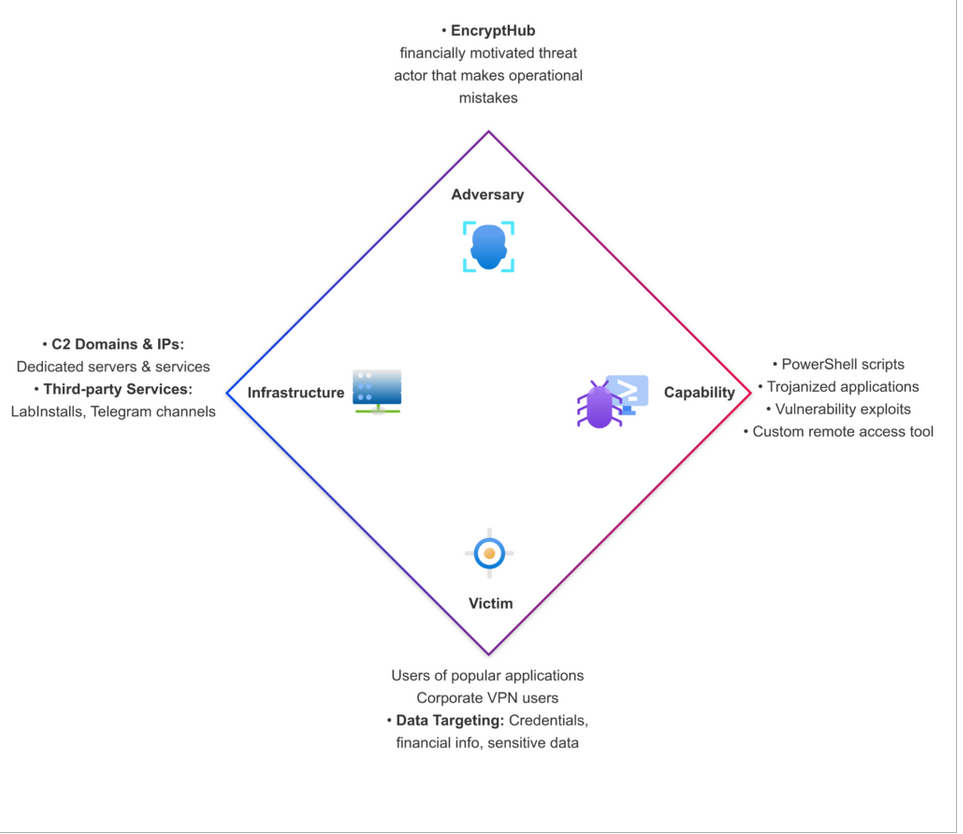
In a latest in-depth investigation, Outpost24’s specialised risk intelligence crew, KrakenLabs, recognized beforehand undisclosed points of a complicated malware operation often called EncryptHub. KrakenLabs’ evaluation, shared with Hackread.com, supplies an in depth understanding of the group’s operational infrastructure, instruments, and attribute behavioural patterns.
This enhanced understanding was made attainable by a collection of safety lapses on the a part of EncryptHub, which, in keeping with Outpost24, inadvertently uncovered essential parts of their malicious ecosystem.
These operational errors embody the enabling of listing listings on their core infrastructure, the storage of stolen knowledge alongside malware recordsdata, and the publicity of Telegram bot configurations used for knowledge theft and marketing campaign oversight.
EncryptHub’s assault campaigns are characterised by multi-layered PowerShell scripts, designed to gather system data, extract helpful knowledge, implement evasion strategies, inject malicious code, and deploy further data-stealing packages. Their distribution strategies embody using trojanized variations of well-liked functions and the employment of third-party pay-per-install companies. The group prioritizes stolen credentials based mostly on components similar to cryptocurrency holdings, company community entry, and VPN utilization.
Moreover, EncryptHub is growing a distant entry device, “EncryptRAT,” which contains a command-and-control panel for managing contaminated techniques, suggesting potential future commercialization. The group additionally actively screens the continued cybersecurity tendencies, integrating newly found vulnerabilities into their assaults.
EncryptHub has examined varied strategies to deploy malware with out detection, together with disguising malicious software program as legit functions. Through the investigation, researchers noticed the group used counterfeit variations of functions like QQ Speak, WeChat, and Microsoft Visible Studio 2022 signed with revoked code-signing certificates, and later with certificates issued by Encrypthub LLC. These trojanized functions contained PowerShell scripts to obtain and execute additional malicious code, gathering system data and deploying knowledge stealers.
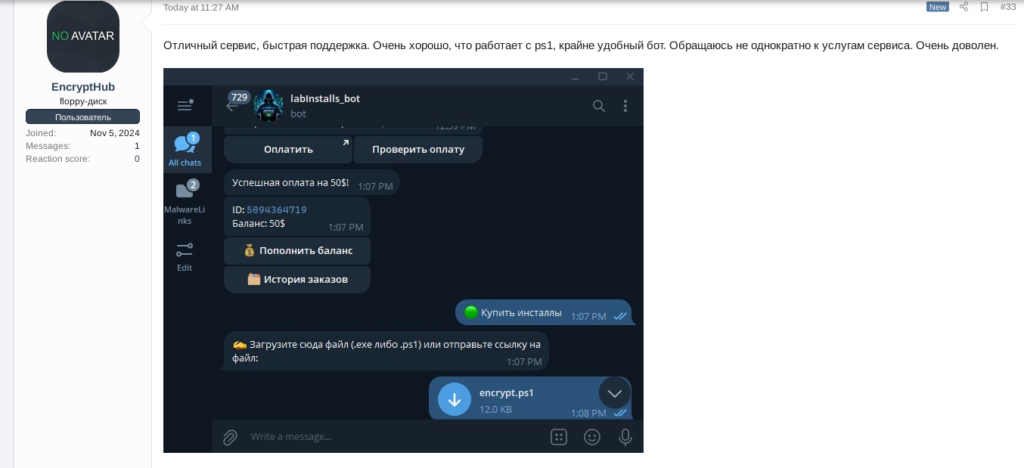
One other distribution technique concerned using LabInstalls, a pay-per-install service, which facilitates the speedy deployment of malware by automated Telegram bots. It’s accessible for as little as $10 (for 100 hundreds) to as much as $450 (for 10,000 hundreds). EncryptHub confirmed their use of this service by suggestions posted on an underground discussion board.
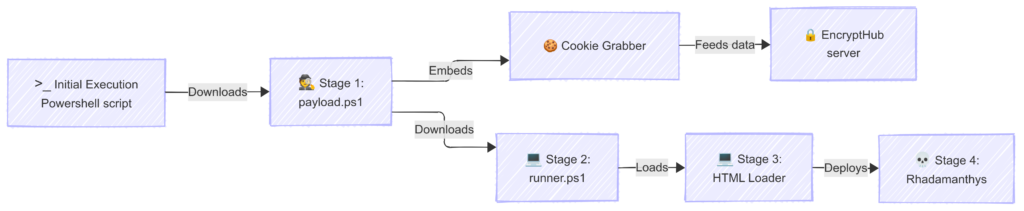
The group’s assault course of, or killchain, has developed, with the most recent model involving a multi-stage PowerShell script execution. The preliminary script steals delicate knowledge, together with messaging periods, cryptocurrency pockets data, and password supervisor recordsdata. It then downloads and executes a second script, which deploys additional malicious elements, together with a modified Microsoft Frequent Console Doc. The ultimate stage includes the deployment of Rhadamanthys, an data stealer.
EncryptHub can also be growing a command-and-control panel, EncryptRAT, which permits for the administration of contaminated techniques, distant command execution, and the monitoring of stolen knowledge. The device’s growth suggests a possible transfer in direction of commercialization, with options like multi-user help and segregated knowledge storage.
KrakenLabs’ findings emphasise the necessity for steady monitoring and enhancing safety measures to counter the evolving threats posed by teams like EncryptHub. The group’s means to adapt and make the most of each in-house instruments and third-party companies highlights the significance of multi-layered safety methods.