
Diffusion fashions like OpenAI’s DALL-E have gotten more and more helpful in serving to brainstorm new designs. People can immediate these programs to generate a picture, create a video, or refine a blueprint, and are available again with concepts they hadn’t thought of earlier than.
However do you know that generative synthetic intelligence (GenAI) fashions are additionally making headway in creating working robots? Latest diffusion-based approaches have generated constructions and the programs that management them from scratch. With or and not using a consumer’s enter, these fashions could make new designs after which consider them in simulation earlier than they’re fabricated.
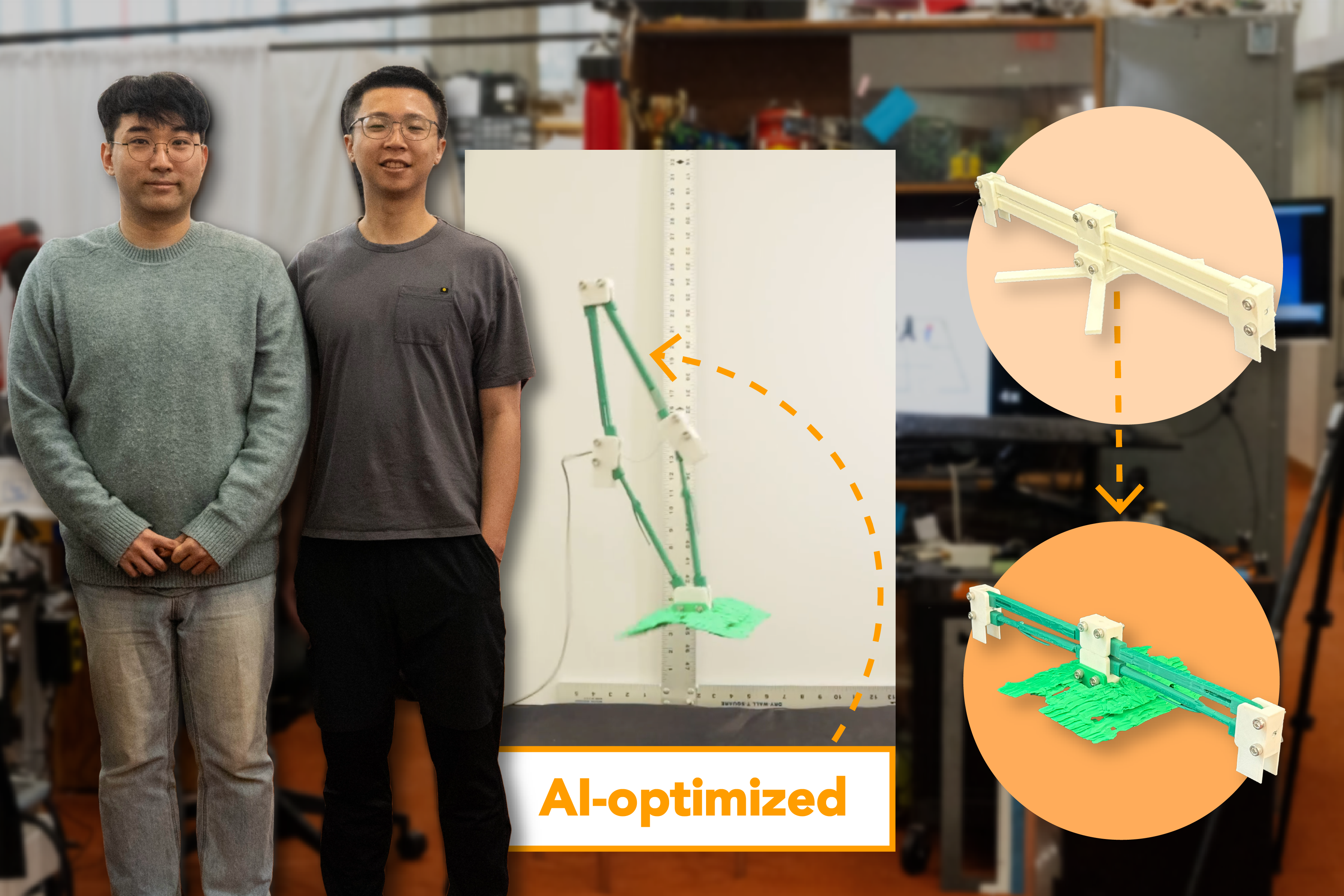
A brand new strategy from MIT’s Pc Science and Synthetic Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) applies this generative know-how towards bettering people’ robotic designs. Customers can draft a 3D mannequin of a robotic and specify which elements they’d wish to see a diffusion mannequin modify, offering its dimensions beforehand. GenAI then brainstorms the optimum form for these areas and assessments its concepts in simulation. When the system finds the correct design, it can save you after which fabricate a working, real-world robotic with a 3D printer, with out requiring further tweaks.
The researchers used this strategy to create a robotic that leaps up a median of roughly 2 ft, or 41 p.c larger than an analogous machine they created on their very own. The machines are practically equivalent in look: They’re each made from a kind of plastic known as polylactic acid, and whereas they initially seem flat, they spring up right into a diamond form when a motor pulls on the twine connected to them. So what precisely did AI do in another way?
A more in-depth look reveals that the AI-generated linkages are curved, and resemble thick drumsticks (the musical instrument drummers use), whereas the usual robotic’s connecting elements are straight and rectangular.
Higher and higher blobs
The researchers started to refine their leaping robotic by sampling 500 potential designs utilizing an preliminary embedding vector — a numerical illustration that captures high-level options to information the designs generated by the AI mannequin. From these, they chose the highest 12 choices primarily based on efficiency in simulation and used them to optimize the embedding vector.
This course of was repeated 5 instances, progressively guiding the AI mannequin to generate higher designs. The ensuing design resembled a blob, so the researchers prompted their system to scale the draft to suit their 3D mannequin. They then fabricated the form, discovering that it certainly improved the robotic’s leaping skills.
The benefit of utilizing diffusion fashions for this process, based on co-lead writer and CSAIL postdoc Byungchul Kim, is that they will discover unconventional options to refine robots.
“We needed to make our machine bounce larger, so we figured we might simply make the hyperlinks connecting its elements as skinny as attainable to make them mild,” says Kim. “Nevertheless, such a skinny construction can simply break if we simply use 3D printed materials. Our diffusion mannequin got here up with a greater concept by suggesting a novel form that allowed the robotic to retailer extra vitality earlier than it jumped, with out making the hyperlinks too skinny. This creativity helped us study in regards to the machine’s underlying physics.”
The workforce then tasked their system with drafting an optimized foot to make sure it landed safely. They repeated the optimization course of, ultimately selecting the best-performing design to connect to the underside of their machine. Kim and his colleagues discovered that their AI-designed machine fell far much less usually than its baseline, to the tune of an 84 p.c enchancment.
The diffusion mannequin’s capability to improve a robotic’s leaping and touchdown expertise suggests it might be helpful in enhancing how different machines are designed. For instance, an organization engaged on manufacturing or family robots might use an analogous strategy to enhance their prototypes, saving engineers time usually reserved for iterating on these adjustments.
The stability behind the bounce
To create a robotic that would bounce excessive and land stably, the researchers acknowledged that they wanted to strike a stability between each objectives. They represented each leaping top and touchdown success charge as numerical information, after which educated their system to discover a candy spot between each embedding vectors that would assist construct an optimum 3D construction.
The researchers observe that whereas this AI-assisted robotic outperformed its human-designed counterpart, it might quickly attain even larger new heights. This iteration concerned utilizing supplies that have been suitable with a 3D printer, however future variations would bounce even larger with lighter supplies.
Co-lead writer and MIT CSAIL PhD scholar Tsun-Hsuan “Johnson” Wang says the mission is a jumping-off level for brand new robotics designs that generative AI might assist with.
“We need to department out to extra versatile objectives,” says Wang. “Think about utilizing pure language to information a diffusion mannequin to draft a robotic that may decide up a mug, or function an electrical drill.”
Kim says {that a} diffusion mannequin might additionally assist to generate articulation and ideate on how elements join, probably bettering how excessive the robotic would bounce. The workforce can be exploring the opportunity of including extra motors to manage which course the machine jumps and maybe enhance its touchdown stability.
The researchers’ work was supported, partially, by the Nationwide Science Basis’s Rising Frontiers in Analysis and Innovation program, the Singapore-MIT Alliance for Analysis and Expertise’s Mens, Manus and Machina program, and the Gwangju Institute of Science and Expertise (GIST)-CSAIL Collaboration. They offered their work on the 2025 Worldwide Convention on Robotics and Automation.





